WA4. Wireshark Capture Analysis¶
Statement¶
You are a network engineer who has been assigned a new client company. Your senior network engineer has informed you that you will be tasked with analyzing the HTTP and TCP traffic flow in the client’s network. This information will be used to improve the performance, security, and general management of the client’s network. Your specific tasks are listed below:
- Start Wireshark capture.
- Open a web browser and visit http://www.example.com/
- Stop the Wireshark capture and answer the following questions with screenshots attached for each:
- a. Identify the TCP 3-way handshake interaction.
- b. What is the MAC address of your PC as shown in Wireshark?
- c. Which vendor manufactured the network card on your PC? Use the PC MAC address as shown in Wireshark.
- d. What is the MAC address of your gateway device as shown in Wireshark?
- e. What is the IP address of your PC as shown in Wireshark?
- f. What version of HTTP is captured?
- g. What is your PC’s operating system (OS) platform as shown in Wireshark?
- h. What language is your PC’s browser configured to as shown in Wireshark?
- You are to save and submit your Wireshark capture file. Add screenshots for all questions from 3a-3h along with their answers in MS Word or PDF file and submit the same.
Answer¶
a. Identify the TCP 3-way handshake interaction¶
To start we need to find the source (my PC) and destination (
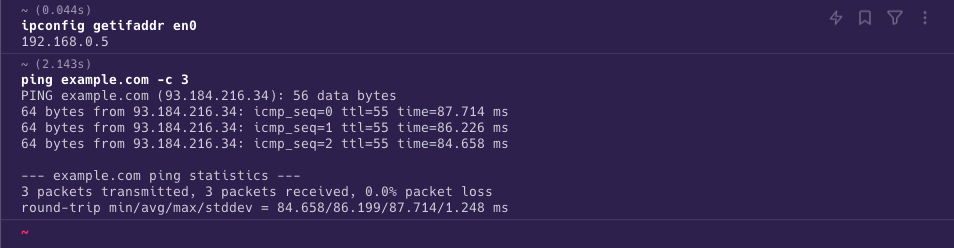
- I ran the command
ipconfig getifaddr en0to find my IP address on MacOS, which is192.168.0.5. - I ran the command
ping www.example.com -c 3to find the IP address of the destination, which isa - Next, we need to find the TCP 3-way handshake interaction; by putting the right filters in Wireshark.
- We use the filter
ip.addr==93.184.216.34to find all packets sent or received to the website’s IP address.
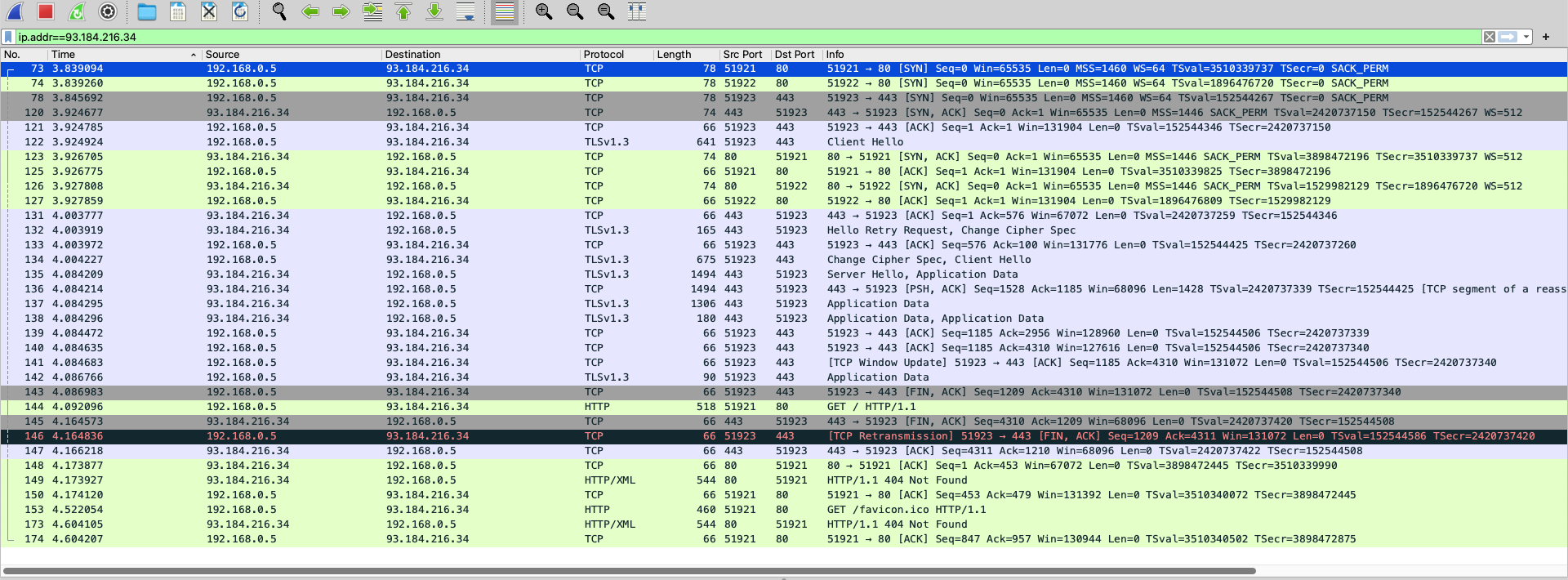
- Examining the packets we see that we have established multiple connections to the website; I guess that I have refreshed the page while capturing the packets.
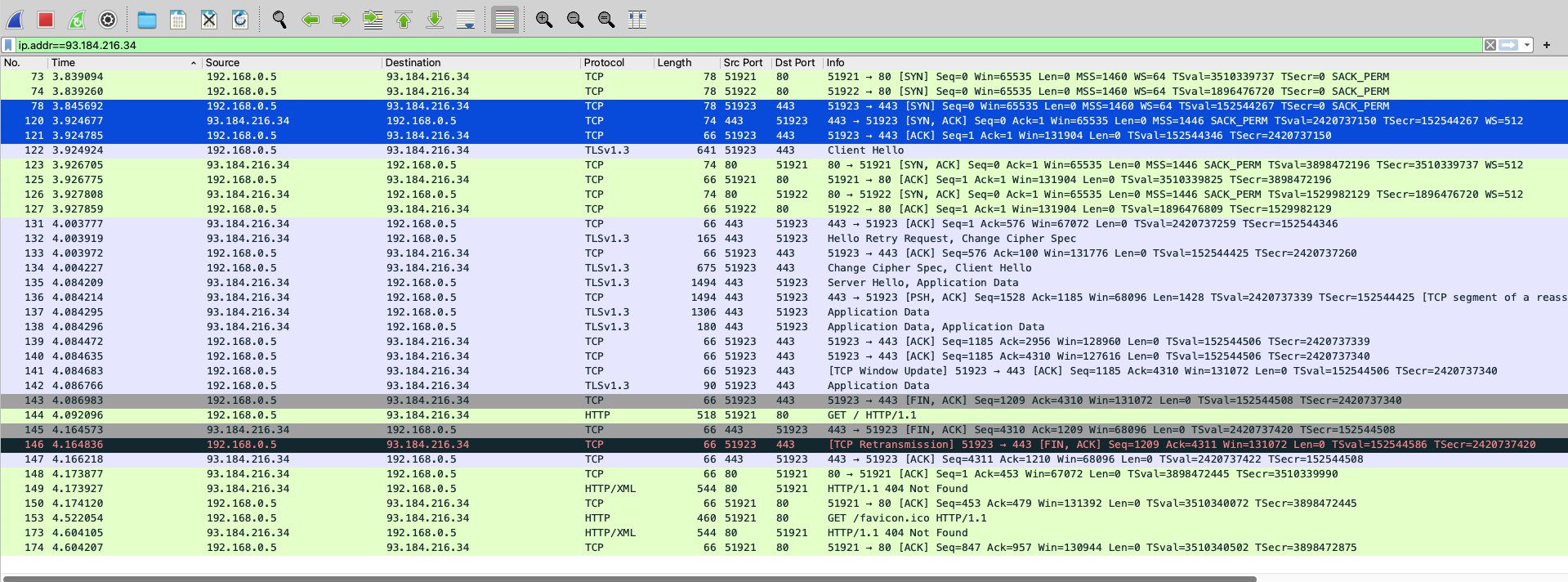
- In the image below, the packets highlighted in blue identified a 3-way handshake interaction; note the
[SYN] Seq=0,[SYN, ACK] Seq=0, and[ACK] Seq=1flags that define the handshake (Upulie, 2022).
b. What is the MAC address of your PC as shown in Wireshark?¶
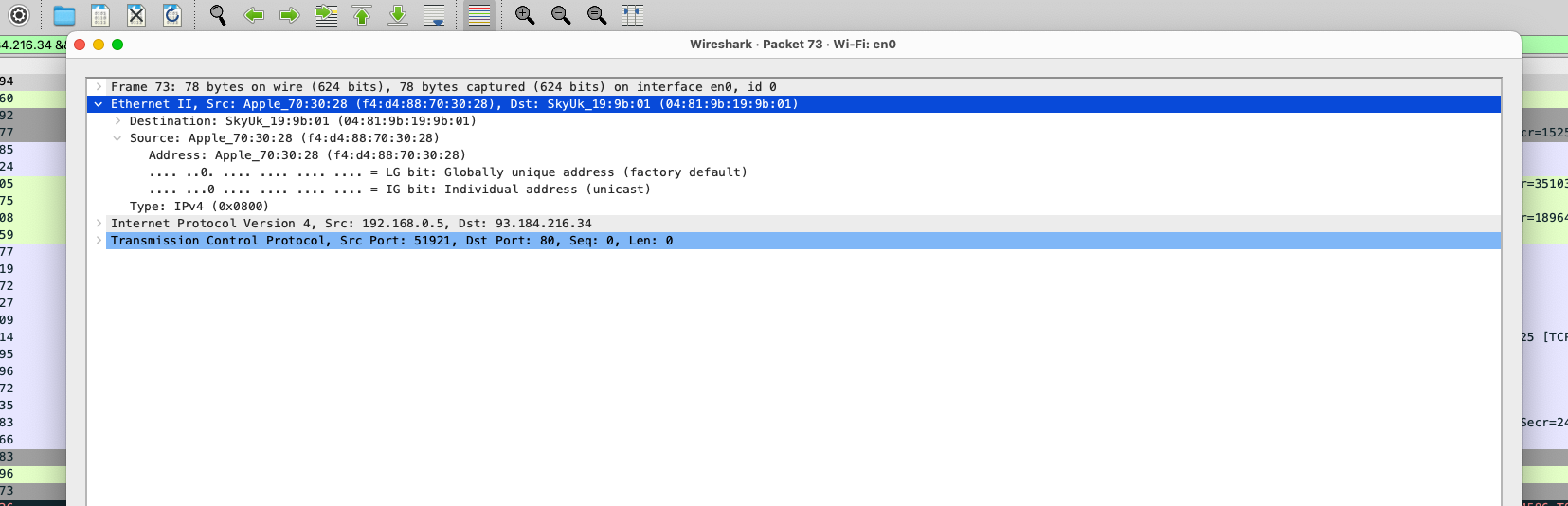
- I selected the first
SYNpacket that was sent from my device, opened the details, and then expanded theEthernet IIsection to find the MAC address of my device. - My MAC address is
Apple_70:30:28 (f4:d4:88:70:30:28)as shown in the image below.
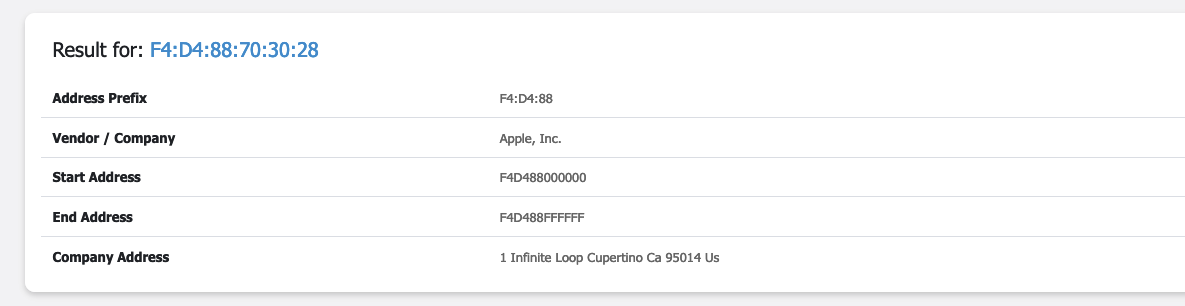
c. Which vendor manufactured the network card on your PC? Use the PC MAC address as shown in Wireshark¶
- The MAC address of my device is
f4:d4:88:70:30:28(from the previous step). - I visited https://dnschecker.org/mac-lookup.php?query=f4%3Ad4%3A88%3A70%3A30%3A28 and entered the MAC address to find the vendor.
- The vendor of my network card is
Apple, Inc.as shown in the image below.
d. What is the MAC address of your gateway device as shown in Wireshark?¶
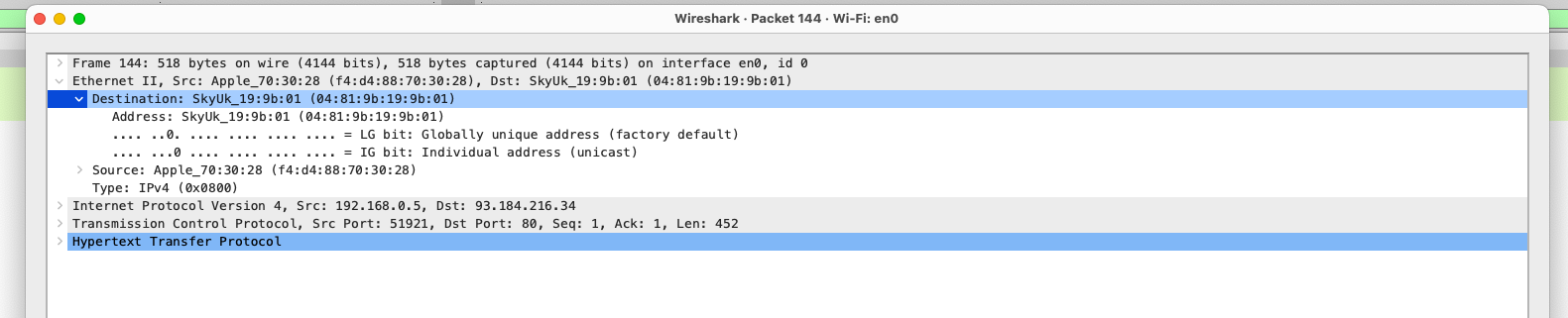
- I used the same
SYNpacket from the previous step and expanded theEthernet IIsection to find the MAC address of the gateway. - The SYN was sent from my device to the gateway, so the destination MAC address is the gateway’s MAC address.
- The MAC address of the gateway is
Destination: SkyUk_19:9b:01 (04:81:9b:19:9b:01)as shown in the image below.
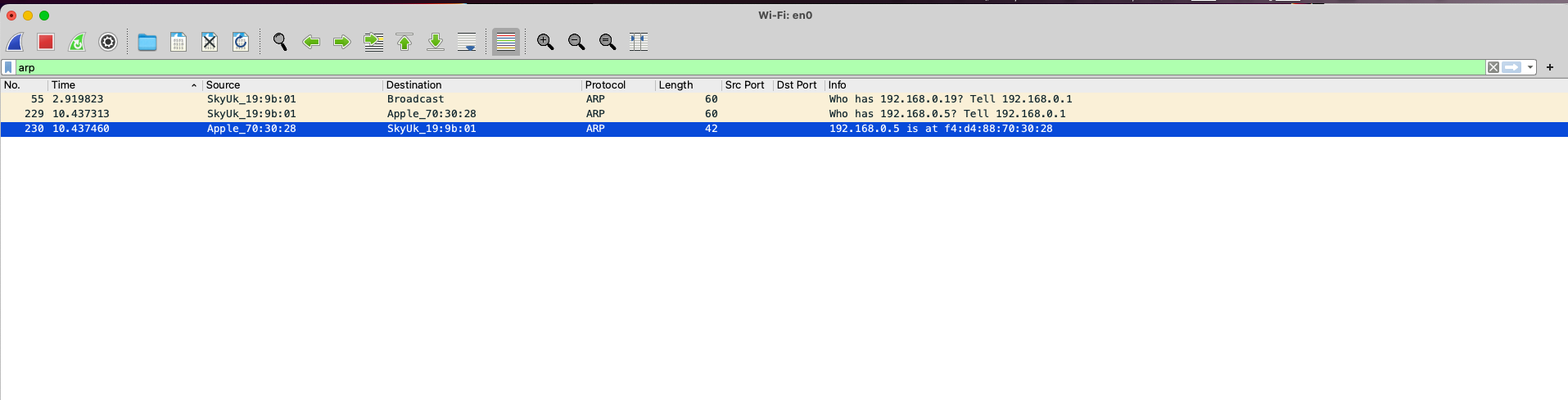
- Another way to find the gateway’s MAC address is to filter for the
ARPprotocol to find the gateway’s MAC address. - You see in the image below the
ARPpackets between my device and the gateway, and the gateway’s MAC address is04:81:9b:19:9b:01.
e. What is the IP address of your PC as shown in Wireshark?¶
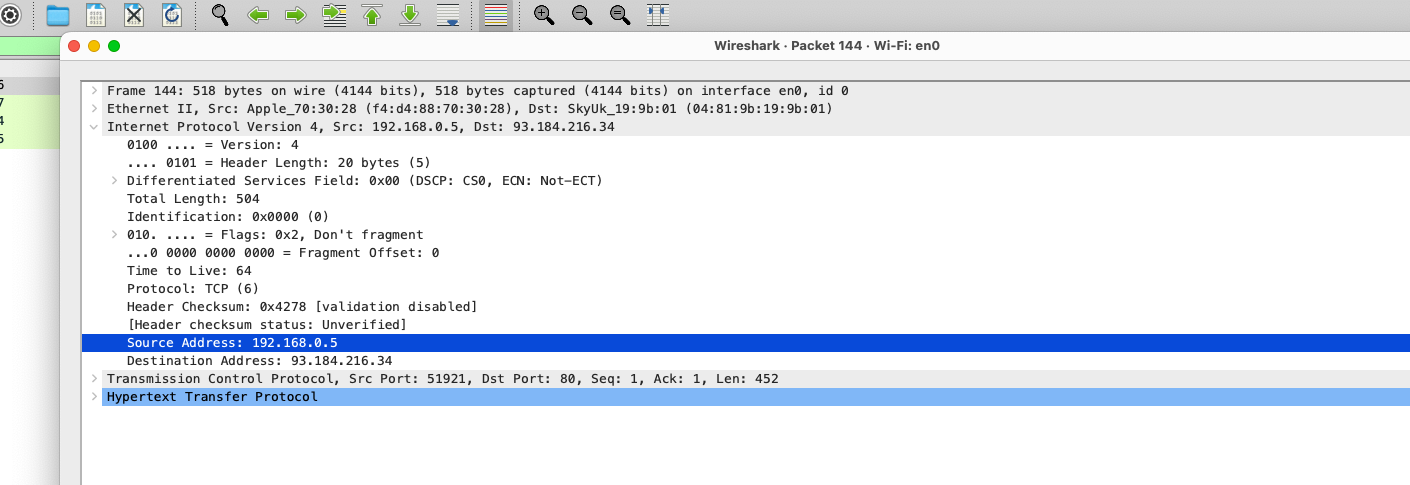
- I filtered for
http, selected the first packet, and then expanded theInternet Protocol Version 4section to find the IP address of my device. - You see my IP address is the Source Address:
192.168.0.5, and it is identical to the one I found using theipconfigcommand (step a).
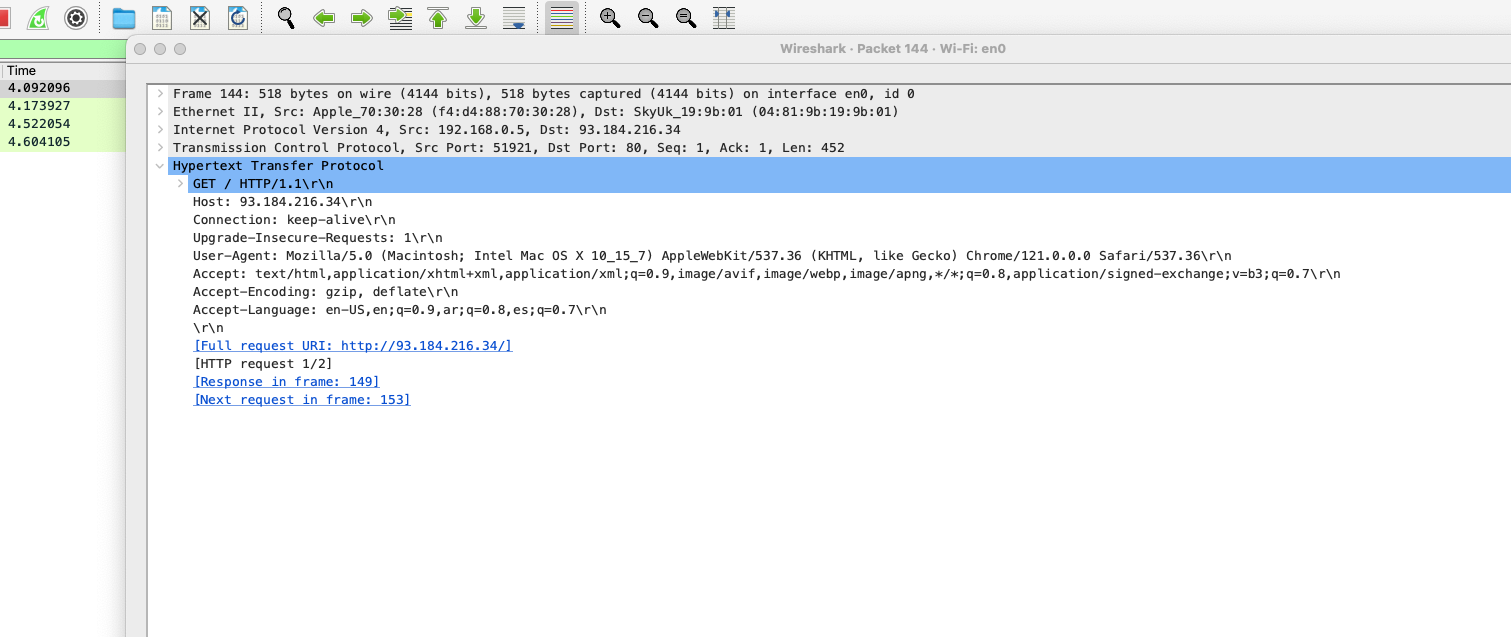
f. What version of HTTP is captured?¶
- I expanded the
Hypertext Transfer Protocolsection of the first packet to find the version of HTTP that was captured. - The version is
HTTP/1.1as shown in the image below.
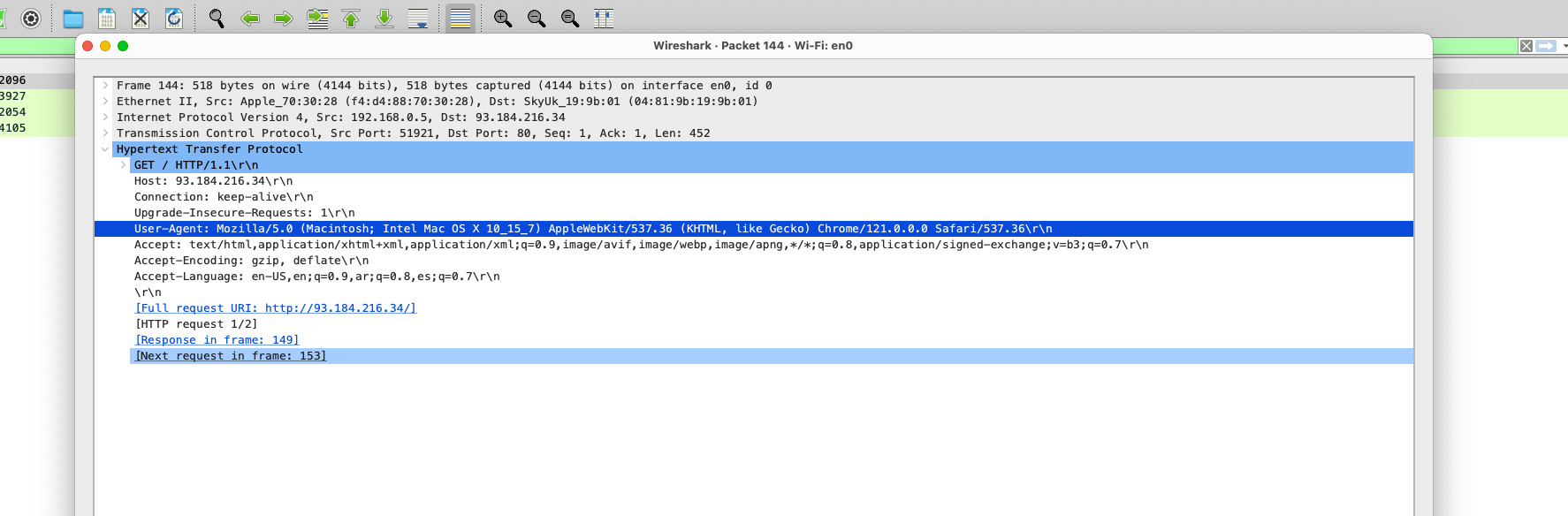
g. What is your PC’s operating system (OS) platform as shown in Wireshark?¶
- I grabbed the
User-Agentfrom the first packet and expanded theHypertext Transfer Protocolsection to find the OS platform. - The OS platform/User-Agent is
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/121.0.0.0 Safari/537.36as shown in the image below.
h. What language is your PC’s browser configured to as shown in Wireshark?¶
- I grabbed the
Accept-Languagefrom the first packet and expanded theHypertext Transfer Protocolsection to find the language. - The language is
en-US,en;q=0.9,ar;q=0.8,es;q=0.7as shown in the image below.
References¶
- UoPeople. (2024). CS 4404 – Written Assignment 4 Instructions. My.uopeople.edu. https://my.uopeople.edu/pluginfile.php/1828160/mod_workshop/instructauthors/CS4404_Unit4_WA_Instructions.pdf
- Upulie H. (2022, July 11). TCP 3-Way Handshake using Wireshark - Upulie Handalage - Medium. Medium; Medium. https://upu.medium.com/tcp-3-way-handshake-using-wireshark-d0c8c7ee4dd2