WA5. IOS Development 1¶
Task 1¶
Install Xcode on your machine and share screenshots of all the steps of installation.
I did not face any difficulties with task as I have XCode installed already as I did some work last year; thus the screenshots below inlcudes the welcome screen and a playground project I created while learning Swift.
Task 2¶
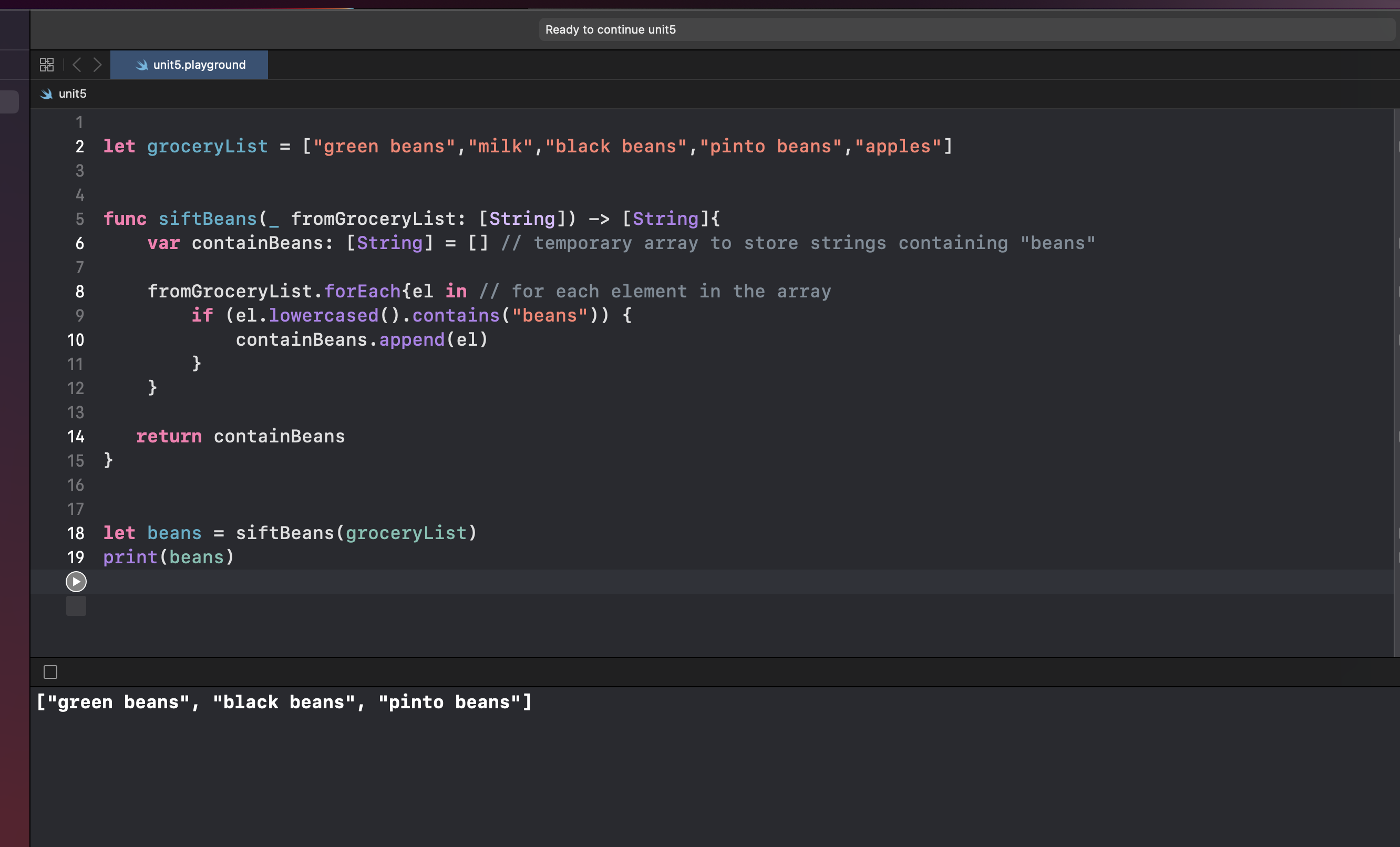
Write a function (which you may name as siftBeans(fromGroceryList:)) that takes a grocery list (as an array of strings) and ‘sifts out’ the beans from the other grocery items.
Input: groceryList = ["green beans","milk","black beans","pinto beans","apples"]
Output should be : ["green beans","black beans","pinto beans"]
let groceryList = ["green beans","milk","black beans","pinto beans","apples"]
func siftBeans(_ fromGroceryList: [String]) -> [String]{
var containBeans: [String] = [] // temporary array to store strings containing "beans"
fromGroceryList.forEach{el in // for each element in the array
if (el.lowercased().contains("beans")) {
containBeans.append(el)
}
}
return containBeans
}
let beans = siftBeans(groceryList)
print(beans)
And the result is in the screenshot below:
Task 3¶
Explain functions in swift and different types of functions – functions without parameters, functions with multiple parameters, functions without return values, and functions with multiple return values. Give examples for each type.
- Functions are self-contained chunks of code that perform a specific task. Swift supports no parameters, named parameters, labeled parameters, default parameters, in-out parameters, nested functions.
- Parameters are named and typed values that functions accept as input when they are called. Swift passes parameters by value by default, unless you specify in-out parameters.
- Functions can also return a value of a specified type. If the function does not return a value, its return type is Void. Void return type can be omitted from the function declaration.
- Both parameters and return values are optional.
Functions without parameters¶
- Functions that do not take any input parameters are called functions without parameters, they still can return a value.
- Calling such function requires empty parentheses after the function name.
func sayHelloWorld() -> String { // no parameters, with return type
return "Hello, world!"
}
print(sayHelloWorld()) // calling the function
function sayHelloWorld() { // no parameters, no return type
print("Hello, world!")
}
sayHelloWorld() // calling the function
Functions with multiple parameters¶
- Functions can have multiple input parameters, which are declared within the function’s parentheses along with their type annotations, separated by commas.
- Parameters can be named, unnamed, or labeled.
- Named: parameters names must be provided when the function is called; along with the parameters value.
- Labeled: parameters labels must be provided when the function is called; along with the parameters value; these labels are names that are used to identify arguments passed to a function.
- Unnamed: By using the
_character as label, the parameter names can be omitted; however, the order that the parameters are passed is important.
func namedParameters(name: String, age: Int) -> String {
return "Hello, \(name), you are \(age) years old!"
}
// named parameters, order does not matter
print(namedParameters(name: "John", age: 21))
func labeledParameters(n name: String, a age: Int) -> String {
return "Hello, \(name), you are \(age) years old!"
}
// labeled parameters, label names were used instead of parameter names
print(labeledParameters(n: "John", a: 21))
func unnamedParameters(_ name: String, _ age: Int) -> String {
return "Hello, \(name), you are \(age) years old!"
}
// unnamed parameters, order matters as the first maps `name` and the second maps `age`
print(unnamedParameters("John", 21))
Functions without return values¶
- As we mentioned, functions with no return type are declared using the special return type
Voidor by omitting the return type declaration altogether. - Functions without return values are called procedures, and they usually perform side effects thus they are not pure functions and can not be assigned to a variable.
- Procedures are usually not recommended in modern programming languages as they are bug prune and hard to test; but they are suitable as entry points to the program or event handlers.
- Performing side effects -usually- involve closures or in-out(aka, passing by reference to work)
var globalCounter = 0
func incrementGlobalCounter () { // no parameters, no return type
globalCounter += 1
}
incrementGlobalCounter()
incrementGlobalCounter()
print(globalCounter) // 2
Functions with multiple return values¶
- Functions that return values can be assigned to a variable, and Tuples are used to capture multiple return values from a function.
func findMinAndMax(arr: [Int])-> (Int, Int) {
let min = arr.min() ?? 0; // default to 0, as min() may return nil
let max = arr.max() ?? 0; // default to 0, as max() may return nil
return (min, max)
}
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
let (min, max) = findMinAndMax(arr: array) // tuple (1, 10)
print(min,max) // 1 10
References¶
- The swift programming language swift 5.7. (n.d.). Apple Inc. https://docs.swift.org/swift-book/LanguageGuide/TheBasics.html